Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Surgery
Price range: ₹1,000.00 through ₹1,800.00
Learn Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Surgery through our scientifically proven stepwise program. You can acquire this skill anywhere, anytime, without quitting your job and daily life.
Please read the Requirements and Commitments of each level before making a purchase. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to receive the product/service.
Description
Orthopaedic surgeons specializing in ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) replacement surgery play a critical role in helping patients with ACL injuries regain knee stability and function. Here’s why it’s important for orthopaedic surgeons to possess the skill to perform ACL replacement surgery:
- Restoration of Knee Stability: ACL injuries can result in knee instability, which can hinder normal activities and sports participation. ACL replacement surgery aims to restore knee stability, enabling patients to return to their desired level of activity.
- Prevention of Further Damage: Prompt ACL reconstruction can help prevent additional damage to the knee joint, such as meniscus tears or cartilage injuries, which can occur due to ACL deficiency.
- Sports Medicine: ACL injuries are common in athletes. Orthopaedic surgeons skilled in ACL reconstruction are valuable in sports medicine, helping athletes return to their sports with confidence.
- Customized Care: Orthopaedic surgeons can provide personalized care by tailoring the ACL reconstruction technique to the patient’s age, activity level, and specific injury characteristics.
ACL Replacement Surgery (ACL Reconstruction) Indication:
ACL replacement surgery, also known as ACL reconstruction, is indicated for individuals who have sustained a torn or ruptured ACL, typically due to sports injuries, falls, or trauma. Common indications include:
- ACL Tear: A complete or partial tear of the anterior cruciate ligament, which causes knee instability and may lead to recurrent episodes of giving way.
- Symptoms: Persistent pain, swelling, instability, and functional limitations in the knee joint due to ACL deficiency.
- Active Individuals: Particularly suitable for active individuals and athletes who wish to return to sports or activities that require knee stability.
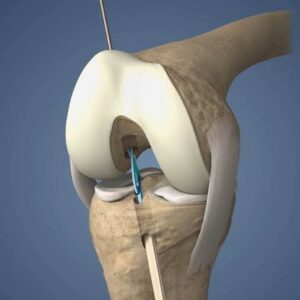
Steps of ACL Replacement Surgery for Orthopaedic Surgeons:
- Patient Preparation: The patient is positioned on the operating table, and the surgical site is prepared and draped in a sterile manner.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made around the knee to access the joint.
- Graft Harvesting: A graft is harvested from either the patient’s own tissue (autograft) or a donor (allograft). Common graft sources include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendons, or cadaveric tissue.
- Graft Preparation: The graft is prepared by removing any excess tissue and shaping it to match the dimensions of the original ACL.
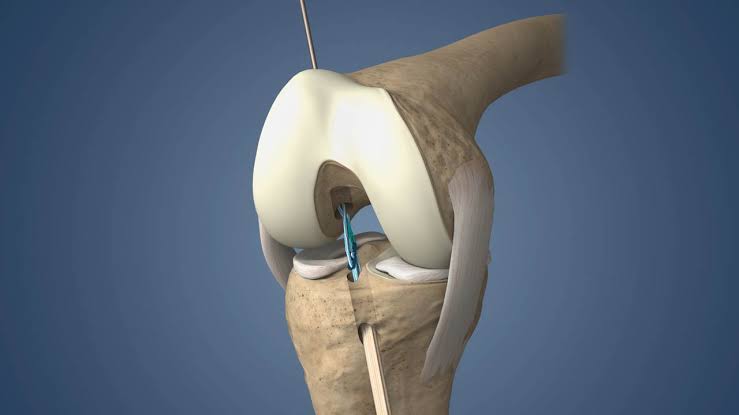
- Tunnel Creation: The surgeon drills tunnels in the tibia and femur to create pathways for the graft.
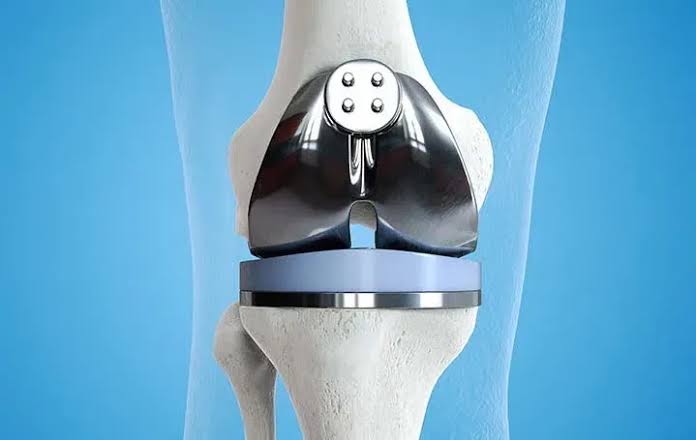
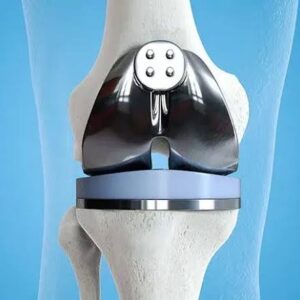
- Graft Fixation: The graft is inserted into the tunnels and secured in place using screws, staples, or other fixation devices.
- Graft Tensioning: The surgeon ensures proper graft tension to replicate the natural function of the ACL.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or staples, and sterile dressings are applied.
- Recovery and Postoperative Care: The patient is monitored in the recovery area and provided with postoperative instructions and rehabilitation guidelines.
Orthopaedic surgeons must be proficient in each of these steps to successfully perform ACL replacement surgery, restore knee stability, and facilitate the patient’s return to an active and functional lifestyle.
Additional information
| Levels | Level-1, Level-2, Level-3 |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.