Arthroscopy
Price range: ₹800.00 through ₹1,600.00
Learn Arthroscopy through our scientifically proven stepwise program. You can acquire this skill anywhere, anytime, without quitting your job and daily life.
Please read the Requirements and Commitments of each level before making a purchase. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to receive the product/service.
Description
Orthopaedic surgeons skilled in arthroscopy play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating various joint conditions. Here’s why it’s essential for orthopaedic surgeons to possess this skill:
- Minimally Invasive: Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, reducing patient trauma, pain, and recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Arthroscopy provides direct visualization of joint structures, enabling precise diagnosis and targeted treatment.
- Versatility: Orthopaedic surgeons can use arthroscopy to treat a wide range of joint issues, including injuries, tears, and degenerative conditions.
Arthroscopy Indication:
Arthroscopy is indicated for patients with joint conditions such as:
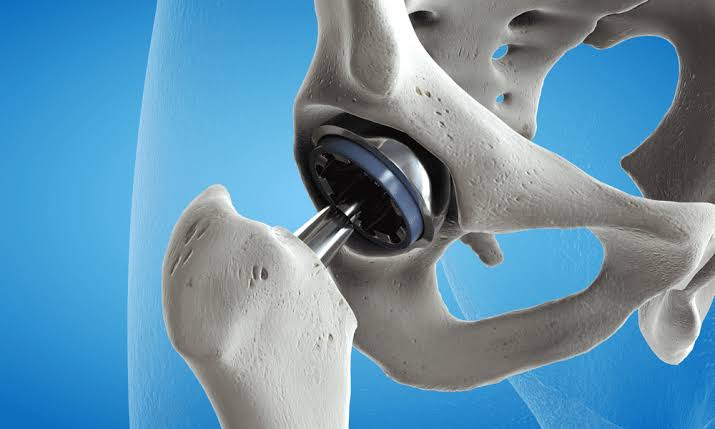
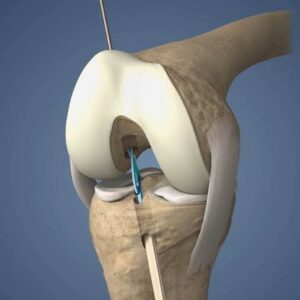
- Torn Cartilage: Meniscus tears in the knee or labral tears in the shoulder or hip.
- Damaged Ligaments: Injuries to the ACL, PCL, or other ligaments in the knee or shoulder.
- Synovitis: Inflammation of the synovial lining in joints.
- Loose Bodies: Floating fragments or debris within the joint.
Steps of Arthroscopy for Orthopaedic Surgeons:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is positioned appropriately for access to the affected joint.
- Anesthesia: Local or regional anesthesia is administered to numb the joint area.
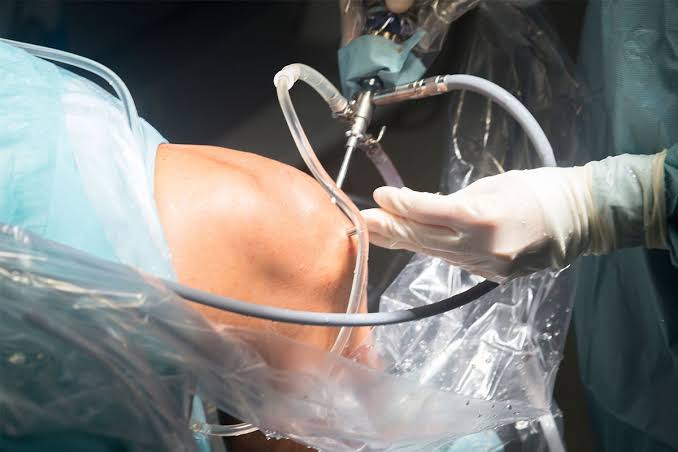
- Incisions: Small incisions (portals) are made near the joint, through which the arthroscope and instruments are inserted.
- Visualization: An arthroscope, a thin tube with a camera and light source, is inserted to visualize the joint’s interior.
- Treatment: Surgical instruments are inserted through additional portals to perform repairs, remove damaged tissue, or address the issue.
- Rinse and Closure: Saline is used to irrigate the joint, and the portals are closed with sutures or staples.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: Postoperative care and rehabilitation are provided to optimize healing and function.
Orthopaedic surgeons must master these steps to successfully perform arthroscopy, offering patients minimally invasive solutions for joint problems, quicker recovery, and improved outcomes.
Additional information
| Levels | Level-1, Level-2, Level-3 |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.