Hip Replacement Surgery
Price range: ₹1,000.00 through ₹1,800.00
Learn Hip Replacement Surgery through our scientifically proven stepwise program. You can acquire this skill anywhere, anytime, without quitting your job and daily life.
Please read the Requirements and Commitments of each level before making a purchase. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to receive the product/service.
Description
Orthopaedic surgeons specializing in hip replacement surgery play a vital role in restoring mobility and improving the quality of life for patients with debilitating hip joint conditions. Here’s why it’s crucial for orthopaedic surgeons to possess the skill to perform hip replacement surgery:
- Pain Relief: Hip replacement surgery offers effective pain relief for individuals suffering from chronic hip pain, allowing them to regain their comfort and mobility.
- Enhanced Mobility: It restores hip joint function, enabling patients to regain the range of motion and strength necessary for daily activities, work, and physical pursuits.
- Improved Quality of Life: For patients with severe hip joint conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or hip fractures, hip replacement surgery can significantly enhance their overall quality of life.
- Customized Care: Orthopaedic surgeons with hip replacement skills can provide personalized care and treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs and objectives.
Hip Replacement Surgery Indications:
Hip replacement surgery, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is indicated for patients with various hip joint conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common indication, where the hip joint’s cartilage gradually wears away, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammatory arthritis that can lead to hip joint damage and loss of function.
- Avascular Necrosis: A condition in which the blood supply to the femoral head (the ball of the hip joint) is compromised, leading to joint destruction.
- Hip Fractures: Particularly in older adults, hip fractures often require hip replacement surgery for optimal recovery.
- Congenital Hip Disorders: In cases where congenital hip disorders result in severe joint deformities and dysfunction.
Steps of Hip Replacement Surgery for Orthopaedic Surgeons:
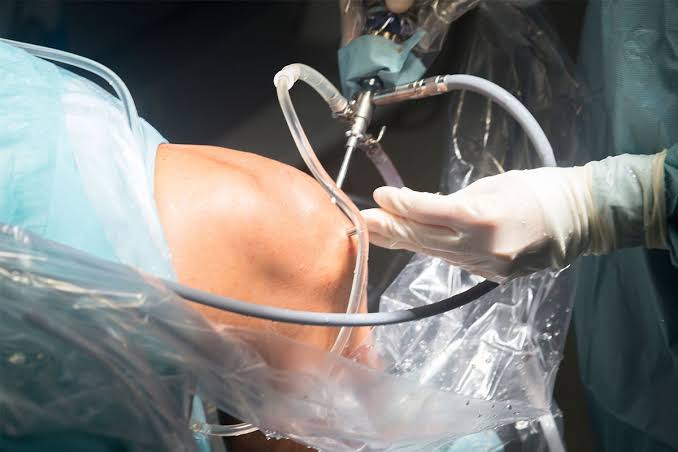
- Patient Positioning: The patient is positioned on the operating table, usually in a lateral or supine position.
- Incision: An incision is made over the hip joint, providing access to the damaged hip joint.
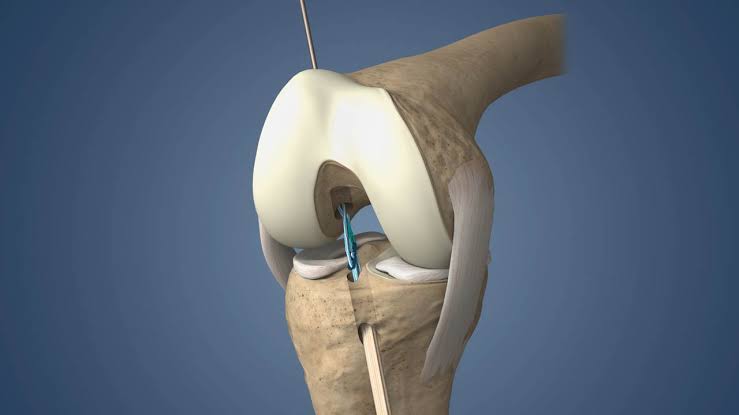
- Femoral Resection: The surgeon removes the damaged or arthritic portion of the femur (thigh bone), preparing it for the femoral component of the implant.
- Acetabular Preparation: If needed, the surgeon prepares the acetabulum (hip socket) by removing damaged cartilage and bone. An acetabular component may be implanted.
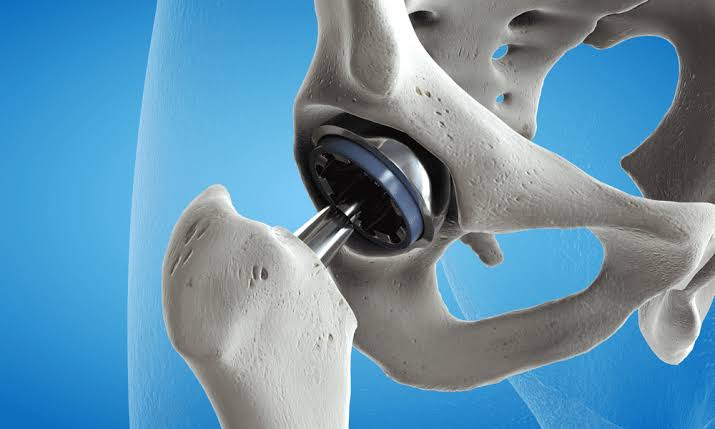
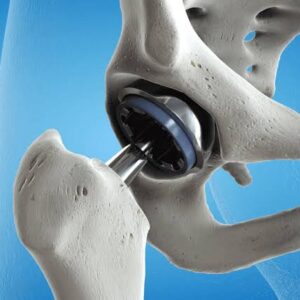
- Implant Placement: The femoral component and acetabular component, typically made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials, are implanted to replace the damaged joint surfaces.
- Stability and Range of Motion: The surgeon assesses the implant’s stability and ensures proper range of motion in the hip joint.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and sterile dressings are applied.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: The patient is closely monitored in the recovery area and provided with postoperative care instructions and a rehabilitation plan.
Orthopaedic surgeons must be proficient in each of these steps to successfully perform hip replacement surgery, alleviate pain, restore function, and enhance the patient’s overall hip joint health.
Additional information
| Levels | Level-1, Level-2, Level-3 |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.