Lower GI Endoscopy Or Colonoscopy
Price range: ₹800.00 through ₹1,600.00
Learn Lower GI Endoscopy Or Colonoscopy through our scientifically proven stepwise program. You can acquire this skill anywhere, anytime, without quitting your job and daily life.
Please read the Requirements and Commitments of each level before making a purchase. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to receive the product/service.
Description
Lower GI Endoscopy, commonly known as colonoscopy, is a vital procedure for physicians and surgeons. Its significance lies in:
- Early Detection: Colonoscopy enables the early detection of colorectal cancer, one of the most prevalent and treatable cancers.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: It offers a highly accurate means of diagnosing various lower gastrointestinal conditions, including polyps, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticulosis.
- Therapeutic Intervention: Physicians and surgeons can perform therapeutic procedures during colonoscopy, such as polyp removal and biopsy, helping to prevent and treat conditions.
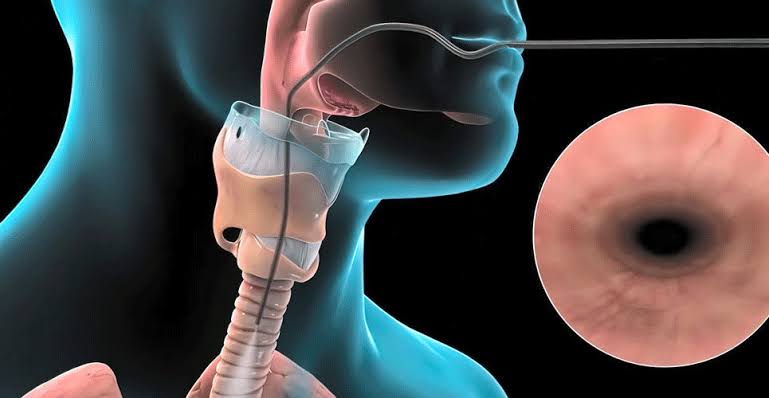
Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy):
Colonoscopy is a procedure that uses a flexible, lighted tube with a camera (colonoscope) to examine the colon and rectum.
Indications for Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy):
- Colorectal Cancer Screening: For routine screening to detect and prevent colorectal cancer.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: To investigate unexplained symptoms like rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits.
- Therapeutic Intervention: For the removal of precancerous polyps and the treatment of certain lower GI conditions.
Steps of Lower GI Endoscopy (Colonoscopy) for Surgeons and Physicians:
- Patient Preparation: Bowel preparation is essential to ensure a clear view of the colon. The patient is usually sedated or given pain relief.
- Insertion: The colonoscope is inserted through the rectum and advanced through the colon.
- Visualization: The physician or surgeon examines the colon’s lining, looking for abnormalities like polyps or tumors.
- Biopsy and Polyp Removal: If necessary, biopsies are taken or polyps are removed using specialized instruments.
- Withdrawal: The colonoscope is slowly withdrawn while observing for any additional findings.
- Post-procedure Care: The patient is monitored as they recover from sedation or anesthesia.
Colonoscopy is an essential tool for the early detection and management of colorectal conditions. Physicians and surgeons proficient in this procedure contribute significantly to patients’ well-being by preventing, diagnosing, and treating lower GI issues.
Additional information
| Levels | Level-1, Level-2, Level-3 |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.