Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Price range: ₹1,000.00 through ₹1,800.00
Learn Shoulder Replacement Surgery through our scientifically proven stepwise program. You can acquire this skill anywhere, anytime, without quitting your job and daily life.
Please read the Requirements and Commitments of each level before making a purchase. Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to receive the product/service.
Description
Orthopaedic surgeons skilled in shoulder replacement surgery play a crucial role in helping patients with severe shoulder joint conditions regain mobility, reduce pain, and improve their overall quality of life. Here’s why it’s important for orthopaedic surgeons to possess the skill to perform shoulder replacement surgery:
- Pain Relief: Shoulder replacement surgery provides effective pain relief for individuals with chronic shoulder pain and dysfunction, allowing them to perform daily activities more comfortably.
- Functional Restoration: It restores shoulder joint function, enabling patients to regain the range of motion and strength needed for daily activities, work, and recreational pursuits.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: For patients with severe shoulder joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injuries, shoulder replacement surgery can significantly enhance their overall quality of life.
- Specialized Care: Orthopaedic surgeons with shoulder replacement skills can offer specialized care and personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual needs and goals of their patients.
Shoulder Replacement Surgery Indications:
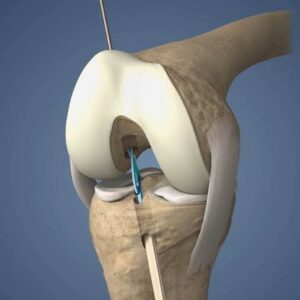
Shoulder replacement surgery, also known as shoulder arthroplasty, is indicated for patients with various shoulder joint conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common indication, where the joint’s cartilage wears away, resulting in pain, stiffness, and loss of function.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammatory arthritis that can damage the shoulder joint and surrounding tissues.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops following a severe shoulder injury, such as fractures or dislocations.
- Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy: A condition characterized by a massive rotator cuff tear and shoulder joint degeneration.
- Avascular Necrosis: A condition where the blood supply to the humeral head (ball of the shoulder joint) is compromised, leading to joint destruction.
Steps of Shoulder Replacement Surgery for Orthopaedic Surgeons:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is placed in a suitable position for the surgical approach, often in a semi-reclining or beach chair position.
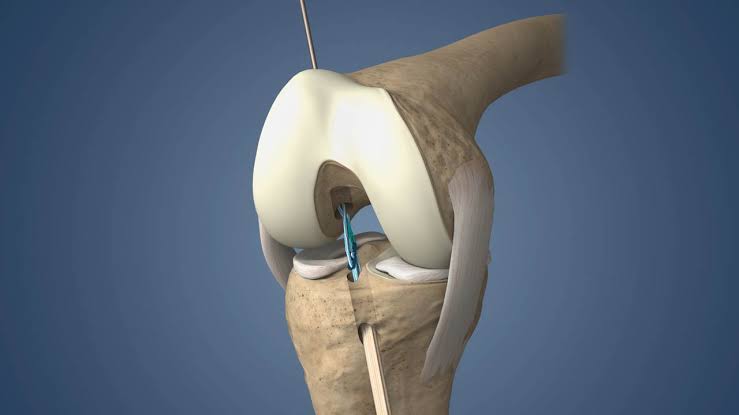
- Incision: An incision is made over the shoulder joint, providing access to the damaged joint.
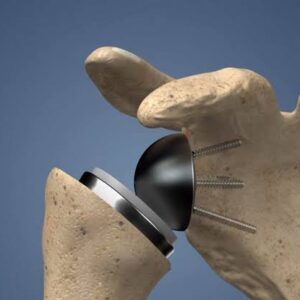
- Humeral Resection: The surgeon removes the damaged portion of the humerus (upper arm bone) to prepare it for the humeral component of the implant.
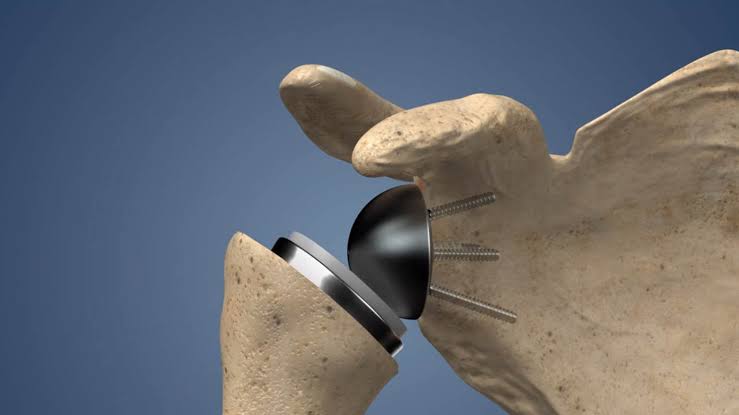
- Glenoid Preparation: If necessary, the surgeon prepares the glenoid (shoulder socket) by removing damaged cartilage and bone. In some cases, a glenoid component may be implanted.
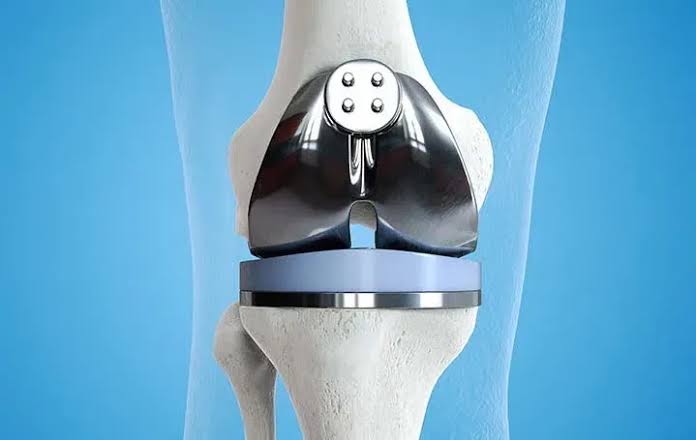
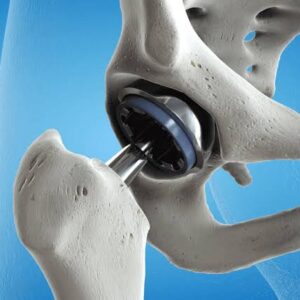
- Implant Placement: The humeral component and, if needed, the glenoid component are implanted. These components are typically made of metal and plastic and replicate the natural shoulder joint surfaces.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and sterile dressings are applied.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: The patient is closely monitored in the recovery area and receives postoperative care instructions and a rehabilitation plan.
Orthopaedic surgeons must be proficient in each of these steps to successfully perform shoulder replacement surgery, alleviate pain, restore function, and improve the patient’s overall shoulder joint health.
Additional information
| Levels | Level-1, Level-2, Level-3 |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.